Section 10.2 the nature of volcanic eruptions answer key – Embarking on a journey through Section 10.2: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions, we delve into the captivating world of volcanic activity. This comprehensive exploration unravels the complexities of volcanic eruptions, shedding light on their diverse forms, influencing factors, and profound impacts.
As we delve deeper, we’ll uncover the mechanisms driving volcanic eruptions, examining the interplay of magma composition, gas content, and tectonic settings. We’ll also explore the diverse array of volcanic landforms, from towering stratovolcanoes to explosive calderas, providing insights into the processes that shape these remarkable landscapes.
Volcanic Eruptions: Section 10.2 The Nature Of Volcanic Eruptions Answer Key

Volcanic eruptions are a fascinating and powerful natural phenomenon that can have a profound impact on the surrounding environment and human populations. They occur when magma, molten rock from deep within the Earth’s crust, rises to the surface and erupts through a vent in the Earth’s crust.
Volcanic eruptions can vary significantly in their nature and intensity, ranging from gentle lava flows to explosive ash plumes that can reach high into the atmosphere.
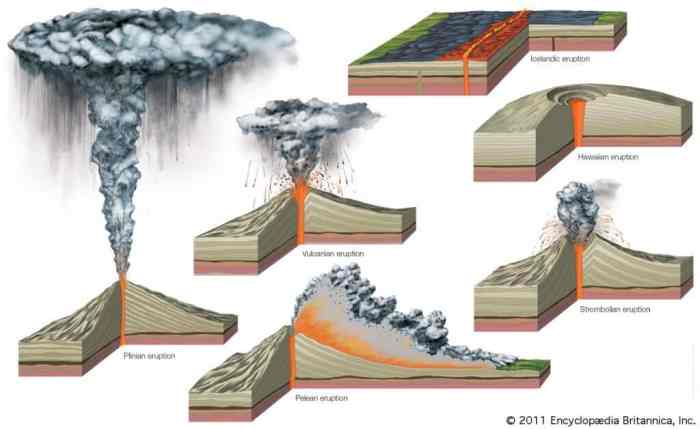
Types of Volcanic Eruptions
- Effusive eruptions: These eruptions are characterized by the outpouring of relatively fluid lava that flows out of the vent and spreads across the surrounding area. Effusive eruptions typically produce lava domes or flows that can travel for several kilometers.
- Explosive eruptions: These eruptions are more violent and involve the ejection of ash, pumice, and other pyroclastic materials into the atmosphere. Explosive eruptions can produce ash clouds that can reach heights of tens of kilometers and can travel thousands of kilometers.
- Phreatomagmatic eruptions: These eruptions occur when magma interacts with water, either from a lake, river, or groundwater. The interaction between the magma and water produces a violent explosion that can eject large amounts of ash and steam into the atmosphere.
Factors Influencing the Nature of Volcanic Eruptions, Section 10.2 the nature of volcanic eruptions answer key
- Magma composition: The composition of the magma plays a significant role in determining the nature of the eruption. Magmas that are rich in silica are more viscous and tend to produce explosive eruptions, while magmas that are low in silica are more fluid and tend to produce effusive eruptions.
- Gas content: The amount of gas dissolved in the magma can also influence the nature of the eruption. Magmas that contain a high concentration of gases are more likely to produce explosive eruptions, as the gases expand and cause the magma to fragment.
- Vent geometry: The shape and size of the vent through which the magma erupts can also affect the nature of the eruption. Narrow vents tend to produce more explosive eruptions, while wider vents tend to produce more effusive eruptions.
FAQ Guide
What are the different types of volcanic eruptions?
Volcanic eruptions can range from effusive eruptions, characterized by gentle lava flows, to explosive eruptions, producing ash clouds and pyroclastic flows.
What factors influence the nature of volcanic eruptions?
Factors such as magma composition, gas content, and tectonic setting play a significant role in determining the explosivity and characteristics of volcanic eruptions.
What are some examples of famous volcanic eruptions?
Notable volcanic eruptions include the 1883 Krakatoa eruption, the 1980 Mount St. Helens eruption, and the ongoing Kīlauea eruption in Hawaii.