As the Northwest Passage allegedly promised a water-route to, it has captivated the imaginations of explorers, scientists, and historians alike. This enigmatic waterway has played a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the globe, fostering both dreams of conquest and scientific discovery.
From the perilous expeditions of early explorers to the modern-day feats of navigation, the Northwest Passage has been a crucible of human endeavor and scientific inquiry, revealing the intricate tapestry of our planet’s geography, oceanography, and climate.
Historical Context
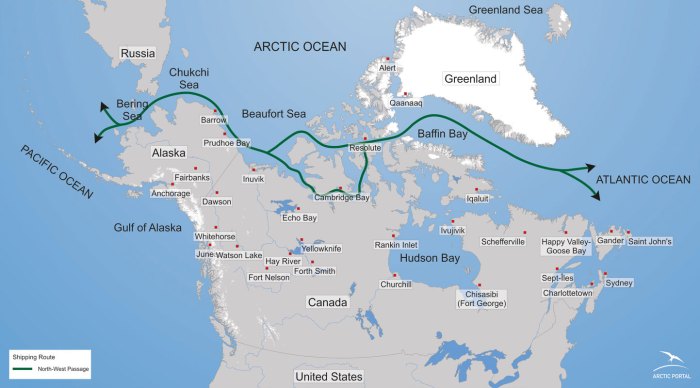
The Northwest Passage held immense significance during the era of exploration. It was believed to provide a shorter and more direct route from Europe to Asia, potentially revolutionizing global trade and geopolitical dynamics. Explorers were driven by the allure of riches, scientific discovery, and the desire to expand their nations’ influence.
Geographical Challenges, The northwest passage allegedly promised a water-route to
Navigating the Northwest Passage presented formidable obstacles. Explorers faced treacherous ice conditions, unpredictable currents, and extreme weather. The icy waters, narrow passages, and unpredictable icebergs posed significant risks to ships and crews.
Exploration Attempts
Numerous expeditions embarked on the quest to find the Northwest Passage. From Martin Frobisher in the 16th century to John Franklin in the 19th century, explorers persisted despite setbacks and failures. Technological advancements, such as improved ships and navigation techniques, gradually increased their chances of success.
Scientific Discoveries: The Northwest Passage Allegedly Promised A Water-route To
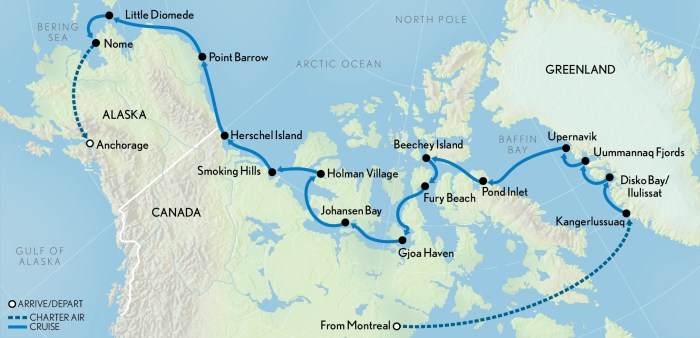
Exploration attempts in the Northwest Passage yielded significant scientific knowledge. Explorers collected data on geography, oceanography, and natural history. Their observations contributed to a better understanding of the Arctic environment, its wildlife, and its impact on global climate patterns.
Economic and Political Implications
The search for the Northwest Passage had far-reaching economic and political consequences. Successful navigation would have shifted trade routes and altered the balance of power between nations. The potential for economic gain and strategic advantage fueled the rivalry among European powers.
Modern Explorations
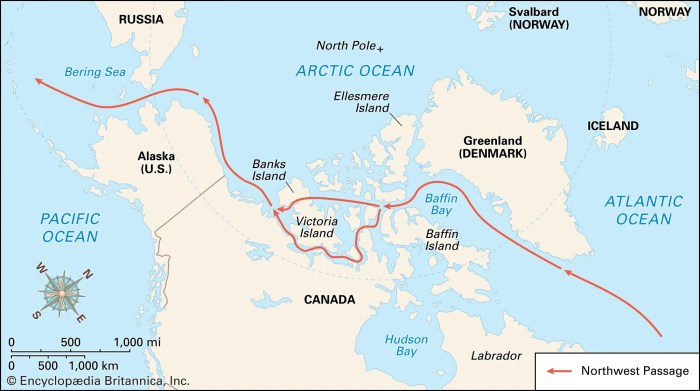
In recent decades, modern technology has facilitated renewed efforts to navigate the Northwest Passage. Improved icebreakers, satellite imagery, and advanced navigation systems have made the passage more accessible. Contemporary expeditions focus on scientific research, environmental monitoring, and the potential for commercial shipping.
Environmental Considerations
Exploration and navigation in the Northwest Passage pose environmental challenges. The melting of sea ice, increased shipping traffic, and potential oil and gas exploration raise concerns about the impact on marine ecosystems, wildlife, and climate change. Balancing scientific and economic interests with environmental protection is crucial.
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of the Northwest Passage?
The Northwest Passage is a legendary sea route connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans through the Arctic archipelago of northern Canada. It has been a sought-after prize for explorers since the 15th century, promising a shorter and more direct route between Europe and Asia.
What are the major challenges of navigating the Northwest Passage?
The Northwest Passage is renowned for its treacherous conditions, including thick ice floes, strong currents, unpredictable weather, and limited visibility. These obstacles have made it historically difficult and dangerous to traverse.
What were the key motivations for exploring the Northwest Passage?
Explorers sought the Northwest Passage for various reasons, including the desire for wealth and glory, the advancement of scientific knowledge, and the expansion of trade and empire.
What scientific discoveries have been made through exploration of the Northwest Passage?
Exploration of the Northwest Passage has contributed significantly to our understanding of geography, oceanography, and natural history. It has led to the discovery of new lands, the mapping of coastlines, and the study of Arctic ecosystems.